<div class="parent">parent
<div class="child">child</div>
</div>
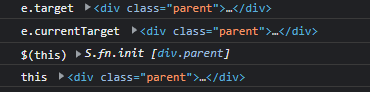
차이를 보기 위해 먼저 .parent 클릭!
// jQuery
$('.parent').on('click', function(e) {
console.log('e.target', e.target);
console.log('e.currentTarget', e.currentTarget);
console.log('$(this)', $(this));
console.log('this', this);
});
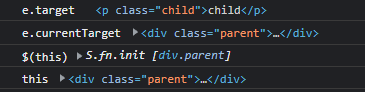
.child 클릭!
// jQuery
$('.parent').on('click', function(e) {
console.log('e.target', e.target);
console.log('e.currentTarget', e.currentTarget);
console.log('$(this)', $(this));
console.log('this', this);
});
확실하게 알아보기.
// jQuery
// 조건: .parent, .child 각각 클릭.
$('.parent').on('click', function(e) {
$(e.target).css({background: 'red'}); // parent child red
$(e.currentTarget).css({background: 'red'}); // parent only red
$(this).css({background: 'red'}); // parent only red
});
currentTarget:: 이벤트 생성 위치 (이벤트 리스너가 달린 요소)target:: 이벤트 발생위치 (실제 이벤트가 발생하는 요소)
target요소는 이벤트버블링에 의해 child가 parent의 이벤트에 영향을 받는다.